Optimize Prompt-Based Custom Models
3 mins read - Updated on Oct 27, 2025Prompt-based Custom Models in Kimola let you build AI models without uploading a dataset — simply by defining labels and describing what each one means. However, the way you write your labels, descriptions, and prompt has a major impact on your model’s accuracy and consistency.
This article will help you understand how to refine and optimize your prompt-based model for better results.
To begin, sign in to your Kimola account and open your dashboard. From the left menu, click Models to access the Models page. On this page, select Create AI Model at the top right corner and choose By Prompt to start building your model.
Refine Your Labels
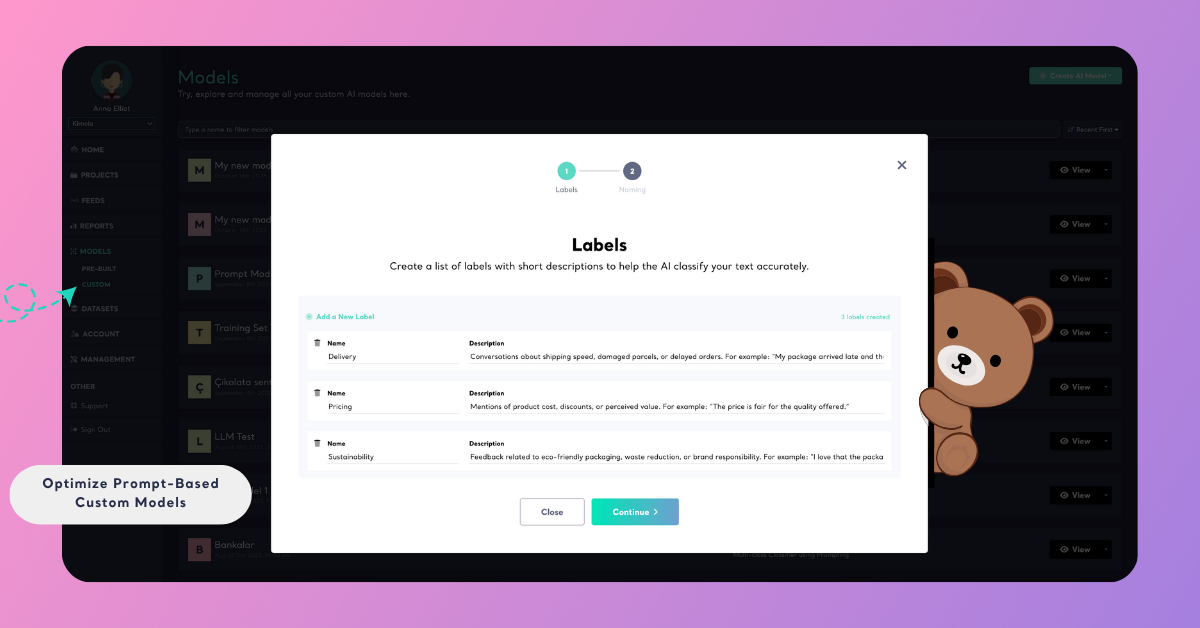
Each label represents a category your model will use to classify text.
The clearer and more distinct your labels are, the more accurately your model will perform.
Follow these guidelines:
- Use clear and unique names: Each label should represent a specific topic or aspect, such as Delivery, Pricing, or Sustainability.
- Avoid overlapping meanings: Don’t include labels that might confuse the AI — Support and Customer Service are too similar.
- Keep names short and neutral: Use nouns or themes, not opinions.
✅ “Delivery” instead of “Late Delivery.”
→ “Delivery” focuses on the topic itself (shipping process, timing, and handling), while “Late Delivery” adds an emotional or judgmental tone. Keeping it neutral helps the AI understand the theme without bias.
or
✅ “Pricing” instead of “Too Expensive.”
→ “Pricing” refers to general discussions about cost, discounts, or perceived value. “Too Expensive” expresses a negative opinion, which can make the AI associate unrelated text with dissatisfaction rather than the price theme itself.
- Limit your label count: For the best accuracy, use between 2 and 25 labels.
Rename any unclear labels before testing your model again. Even small wording changes can significantly improve classification quality.
Improve Label Descriptions
Descriptions help the AI understand what kind of text belongs under each label.
Well-written descriptions act as the real “prompt” for your model — they teach the AI how to interpret your categories.
A good description should:
- Briefly define the theme: Explain what the label represents in one sentence.
- Include examples: Mention what types of feedback or sentences belong to it.
- Avoid repetition: Make sure descriptions differ clearly from one another.
Test and Evaluate
After editing your labels and descriptions, test your model to see how well it performs on real text. You can test it with a single sentence or upload a dataset.
To learn more, see the Test a Custom Model article.
When reviewing results, check:
- If the model classifies similar texts consistently.
- Whether any labels are rarely or never used (a sign they may be unclear).
- If some categories are confused with others — this means their descriptions need more contrast.
When to Rebuild
If your model repeatedly mislabels certain topics or performs inconsistently, it might be time to switch methods. For complex use cases, creating a model with a training dataset can give you more control and accuracy.
To learn how, see Create a Custom Model with a Training Dataset.