Social Feedback Analysis
as it should be
Understand what people are saying about your product or service by analyzing social media conversation and online discussions.
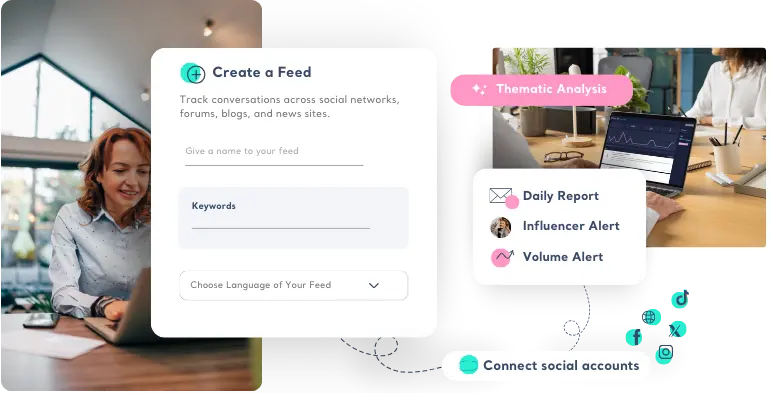
Understand what people are saying about your product or service by analyzing social media conversation and online discussions.
Connect social media accounts to get DM'S, mentions, comments of Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, Youtube and more channels into one platform to track and analyze. Have a social media management tool already? Let us know and we'll integrate.
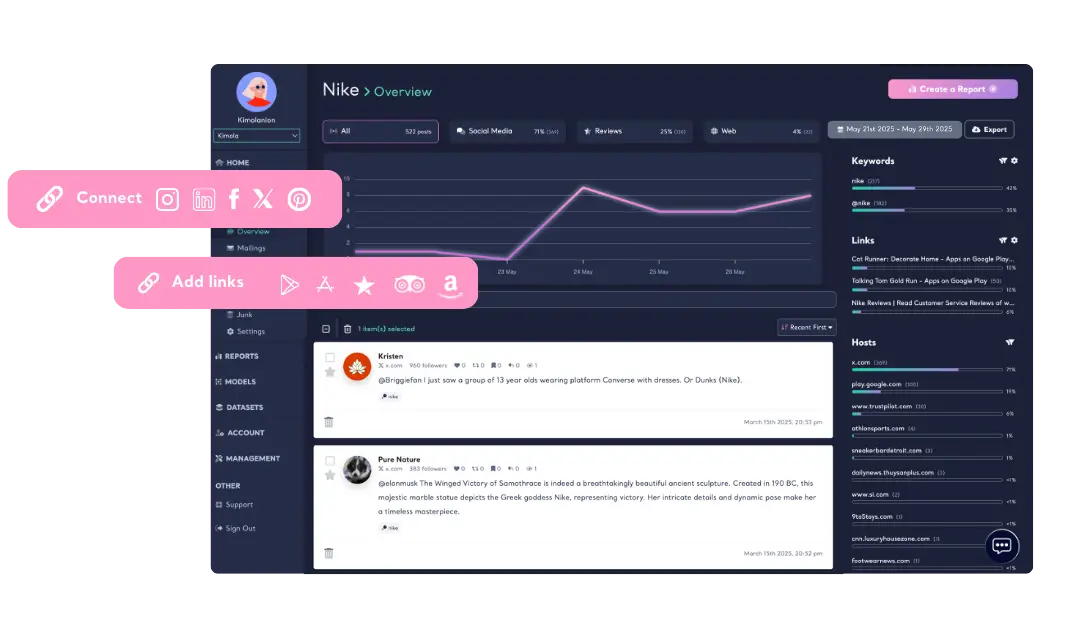
Track brand mentions, customer opinions, and industry trends across social media, forums, and online communities. Use Keyword Tracking to monitor specific terms or Link Tracking to automatically collect reviews from platforms like Trustpilot, TripAdvisor, and Google Business. Stay informed and respond to customer feedback in real time.
If you already have social feedback collected from various sources, Kimola supports direct dataset uploads in Excel, CSV, or TSV formats. Simply map key columns in your dataset to transform scattered feedback into structured, research-ready reports. This ensures that every comment, review, or mention contributes to a deeper understanding of customer needs.

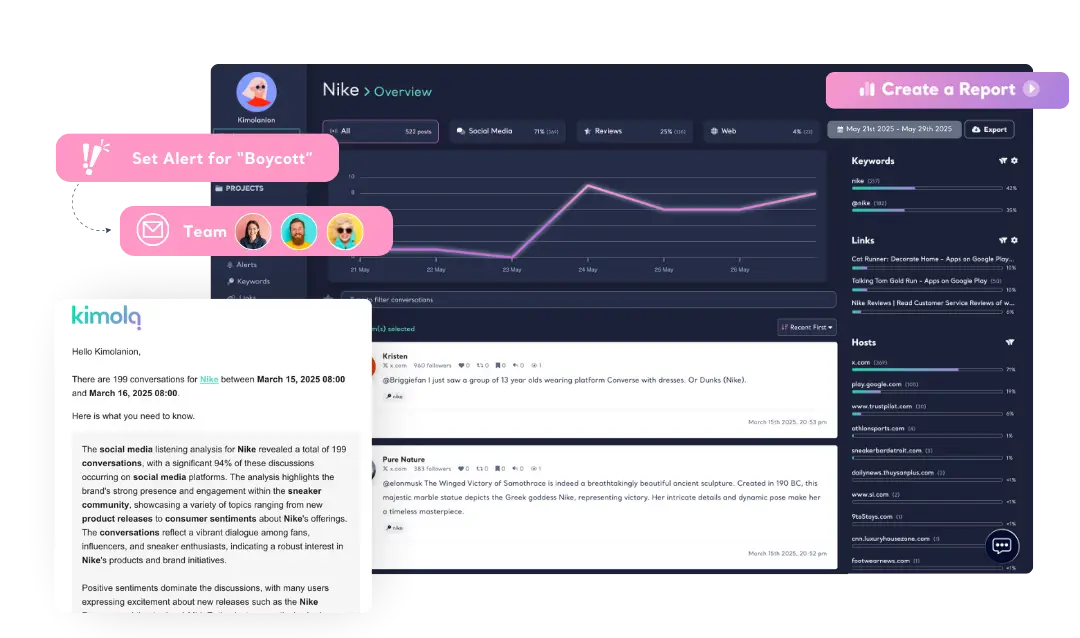
Kimola delivers automated reports in hourly and daily basis to track specific keywords, influence levels, or sudden data spikes. Get notified about 🔔 keyword mentions, 👑 influencer involvements, or 🔺 sudden spikes in the data volume. Each email type has a unique emoji in the subject line, so you can recognize the type of update at a glance—without even opening your inbox.
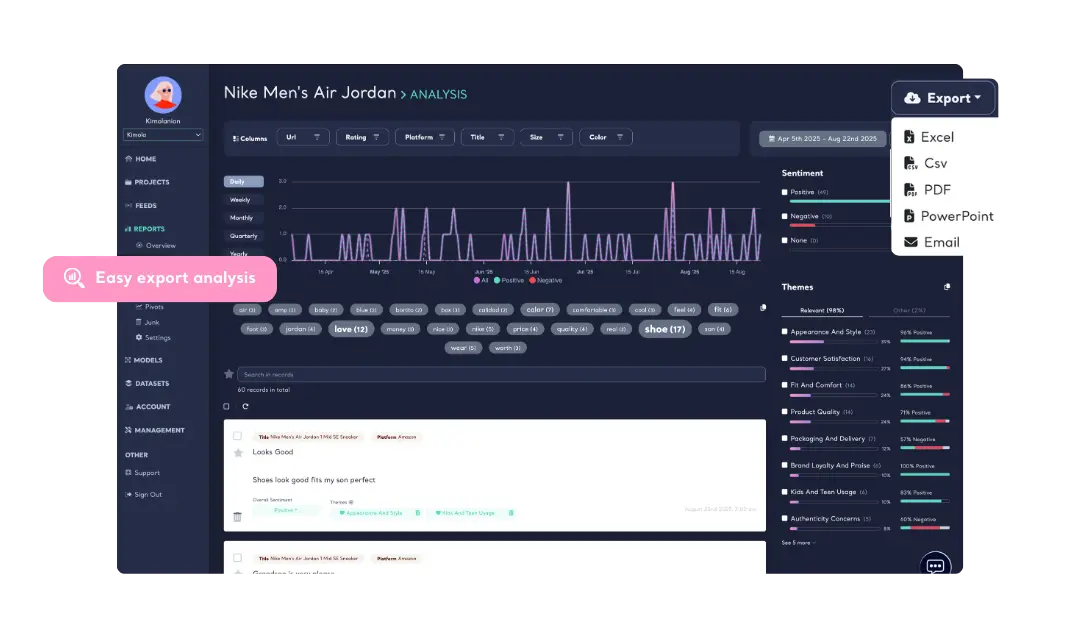
AI-generated executive summaries present key findings in a structured format, making them easy to interpret and act upon.
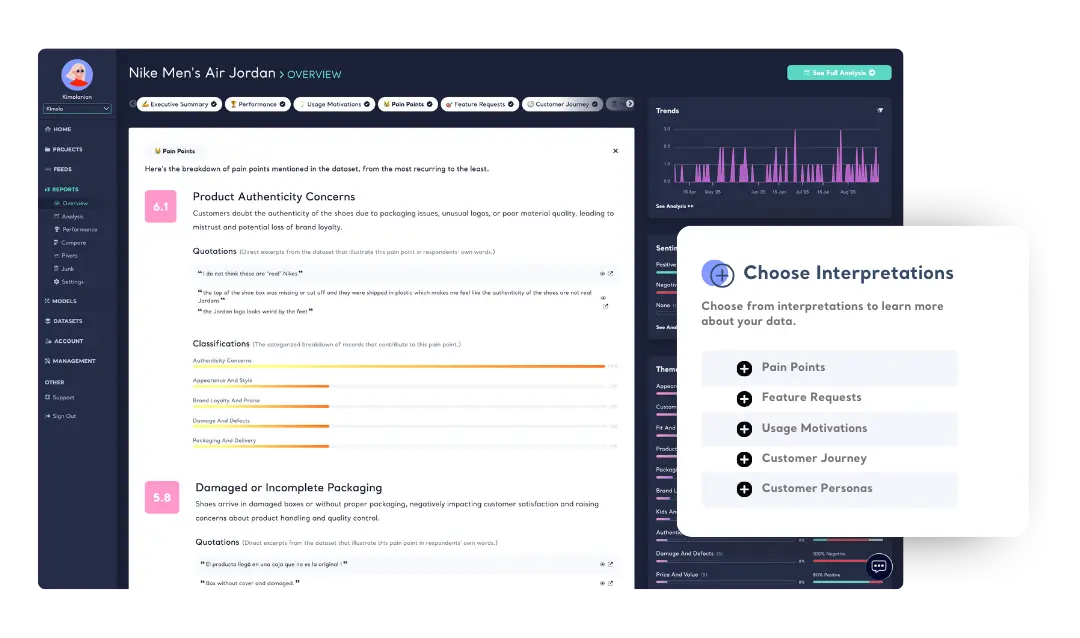
Kimola assigns sentiment for each theme in a single customer feedback, ensuring you capture every detail—what customers like, dislike, and why. Even when a customer mentions different topics within the same review, Kimola successfully breaks down feedback into multiple aspects and accurately assigns sentiment to each, so no insight is lost!
Learn about Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
Kimola's Dynamic Classification™ technology understands context and generates relevant theme clusters without relying on pre-defined categories. It adapts to any dataset, eliminating the need for manual labeling or data annotation. This ensures precise categorization of unstructured feedback from online reviews, surveys, and social media—without human error.

Kimola analyzes social media feedback and turns it into themes, executive summaries, pain points and more to help companies understand the discussion between social media users.
Export social media feedback to Powerpoint, Excel and PDF easily with Kimola.
Collect and centralize feedback.
Make sense of large-scale feedback.
Turn data into meaningful insights.
Find out how Kimola can improve your feedback analysis process.
Uncover customer needs, likes, and dislikes from product reviews and feedback.
Analyze customer reviews and ratings to optimize online shopping experiences.
Extract insights from social media conversations and online discussions.
Make sense of free-text survey responses with AI-powered analysis.
Understand customer sentiment and concerns from chat and call transcripts.
Identify workplace trends and employee sentiment from internal feedback and reviews.
Social Feedback Analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting customer opinions, discussions, and sentiment from social media platforms, forums, and online communities. By understanding these conversations, businesses can gain valuable insights into brand perception, customer expectations, and industry trends.
Customer opinions shared online influence brand reputation, purchasing decisions, and market trends. Social Feedback Analysis helps businesses track public sentiment, detect emerging issues, and uncover opportunities for product or service improvements—leading to better customer engagement and data-driven decision-making.
Kimola enables businesses to track mentions using Keyword Tracking, monitor online discussions through Link Tracking, and upload existing datasets in Excel, CSV, or TSV formats for structured analysis. This ensures all relevant feedback is gathered in one place for seamless insights.
Yes. Kimola supports 30+ languages, making it possible to analyze customer feedback across different regions and languages without barriers.
Yes. With Automated Reports & Alerts, Kimola delivers real-time updates on brand mentions, influencer involvements, and data spikes directly to your inbox, so you don’t have to track conversations manually.
Analyze customer feedback in 30+ languages—no AI training needed.
Create a Free Account No credit card · No commitment Product Feedback Analysis
Product Feedback Analysis
 E-commerce Feedback Analysis
E-commerce Feedback Analysis
 Social Feedback Analysis
Social Feedback Analysis
 Open-ended Survey Analysis
Open-ended Survey Analysis
 Chatbot and Call Center Conversational Analysis
Chatbot and Call Center Conversational Analysis
 Employee Feedback Analysis
Employee Feedback Analysis