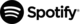Test a Pretrained Model
4 mins read - Updated on Oct 28, 2025A Pretrained Model is an AI model already created and trained by Kimola for specific industries such as E-Commerce, Banking, Automotive, Telecommunications, and more. Unlike Custom Models, pretrained models are ready to use — there’s no need for manual labeling or training.
After selecting a pretrained model, you can test it directly in Kimola to see how it classifies text before applying it to larger datasets. Testing helps you verify how the model interprets your text and ensures it’s the right fit for your analysis needs. You can test a model by manually entering text or by uploading a document for batch testing.
Sign in to your Kimola account and go to the Models section on the left panel. Select the Pre-Built tab and click the model you want to test (for example, E-Commerce Conversations Classifier). This will open the model’s overview page, where you’ll find testing options.
Alternatively, you can also visit the Pretrained AI Models page on Kimola’s website to test models directly from their individual pages.
Test with a Text
If you want to quickly see how your pretrained model interprets text, you can test it with a single sentence or paragraph.
- On your model’s Overview page, find the Text section.
- Type or paste your sample text into the input box, and the model will instantly display the predicted label and sentiment for your input.
This method is ideal for quickly checking if the model correctly understands short samples before running it on larger datasets.
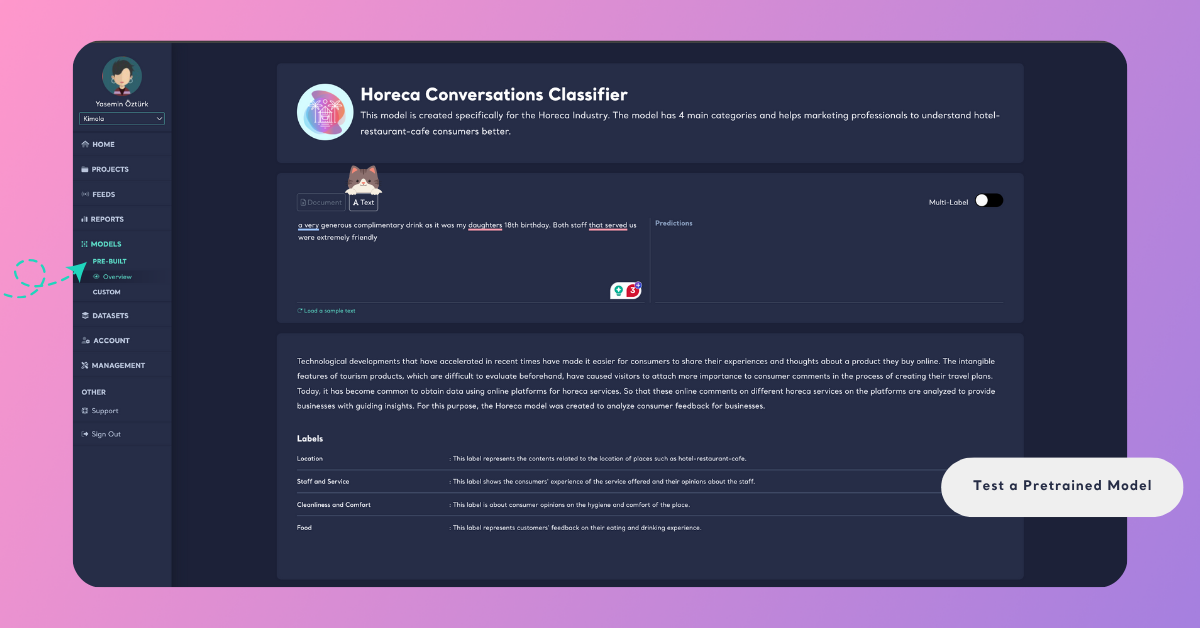
Test with a Document
You can also upload a file to test how your pretrained model performs on multiple records at once.
Step 1: Upload Your Dataset
In the Overview page, open the Document section and upload your dataset by dragging and dropping your file or by clicking Upload Your Dataset. You can upload documents in .xls, .xlsx, .csv, or .tsv format.
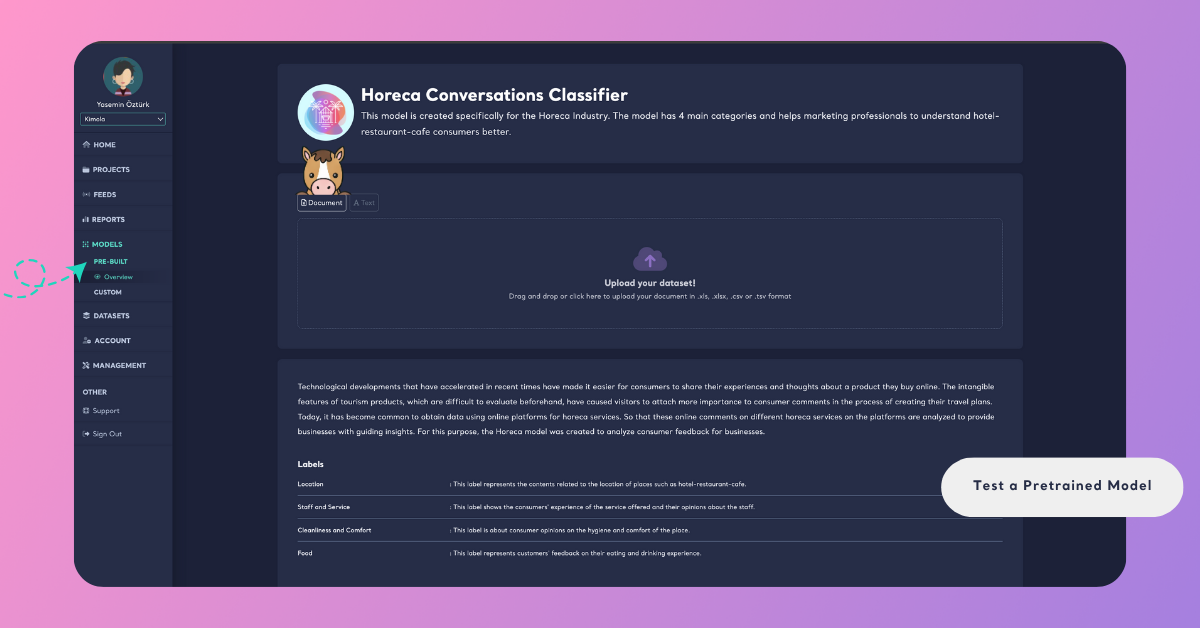
Step 2: Map Your Columns
After uploading, you’ll see a preview of your dataset. Here, map the required columns to continue:
- Content column: The column that contains the text data to be analyzed (e.g., customer feedback, survey responses, product reviews, social media posts, or support tickets).
- URL column: An optional field linking to the source of each record. This can later be used as a filter or to navigate to the original source in your report.
- Date column: An optional field containing the date of each record. Including it helps visualize data trends over time.
Once you complete your selections, proceed to the next step.
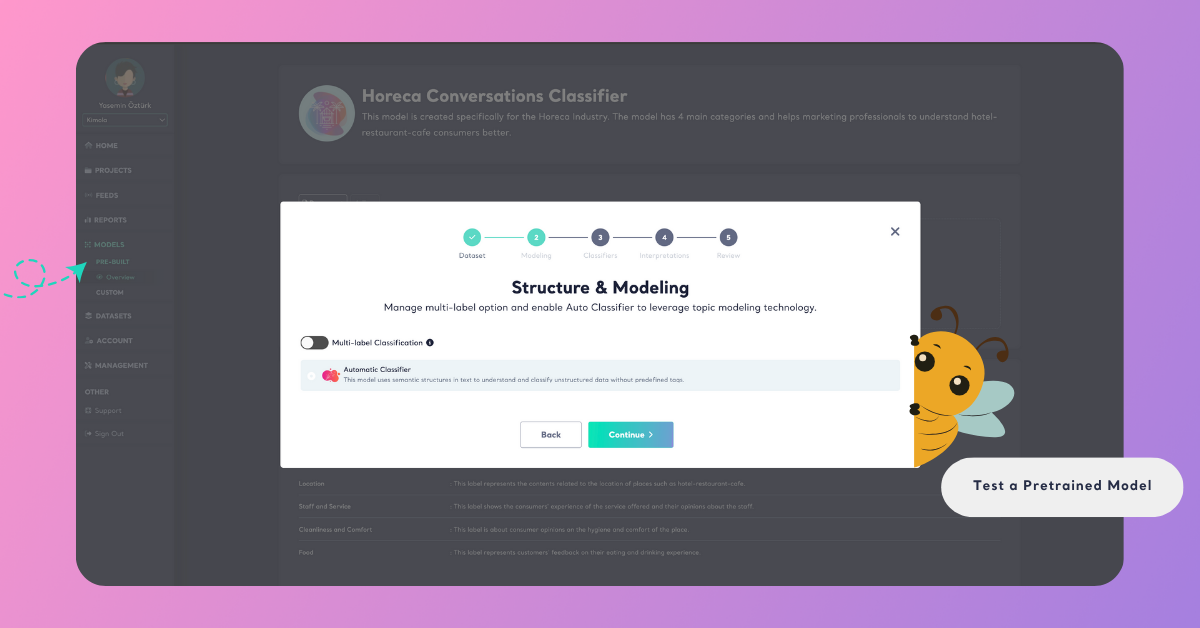
To make sure your test runs only with the selected pretrained model, click Advanced and uncheck Automatic Classifier.
The Automatic Classifier is Kimola’s built-in AI that automatically classifies customer feedback without any setup or training. Disabling it ensures the results come only from the pretrained model you selected.
You can also disable Multi-Label Classification if you want each record to fall under only one category.
When this option is enabled, a single comment can belong to multiple categories — for example:
“Delivery was slow but customer service was excellent.”
→ Delivery and Customer Service
Step 3: Select Interpretations
In the Interpretations step, you can add extra layers of analysis to enrich your results. Besides standard classification, you can have customer feedback interpreted with a research-driven approach — uncovering deeper insights.
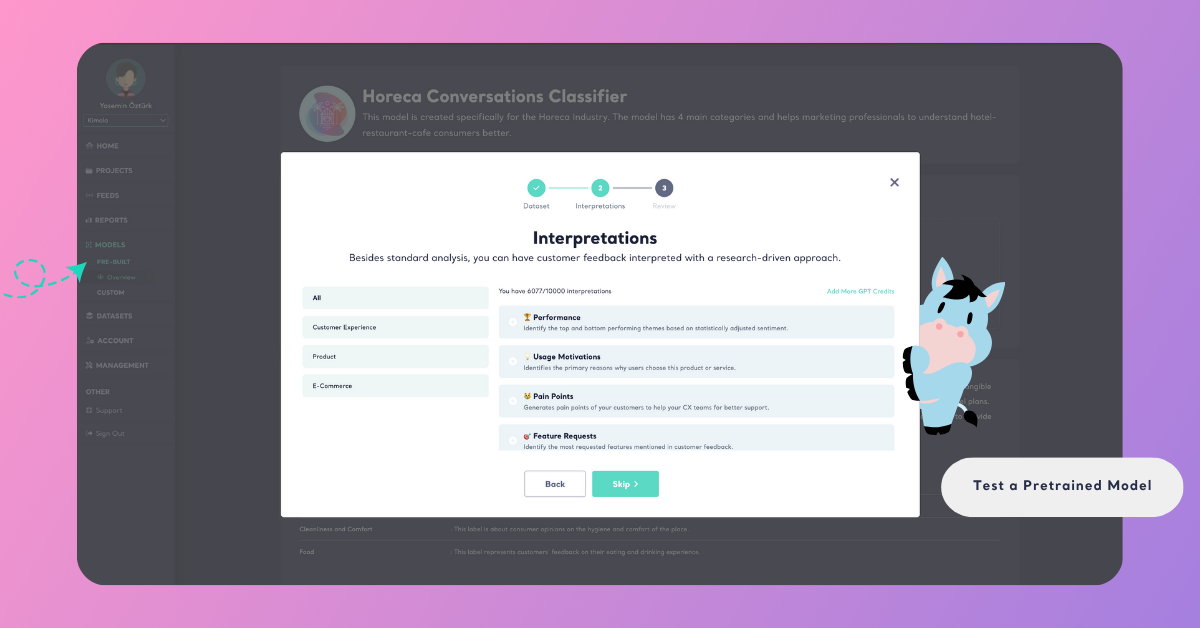
You can select one or more interpretations to include, or skip this step if you prefer to proceed directly to testing.
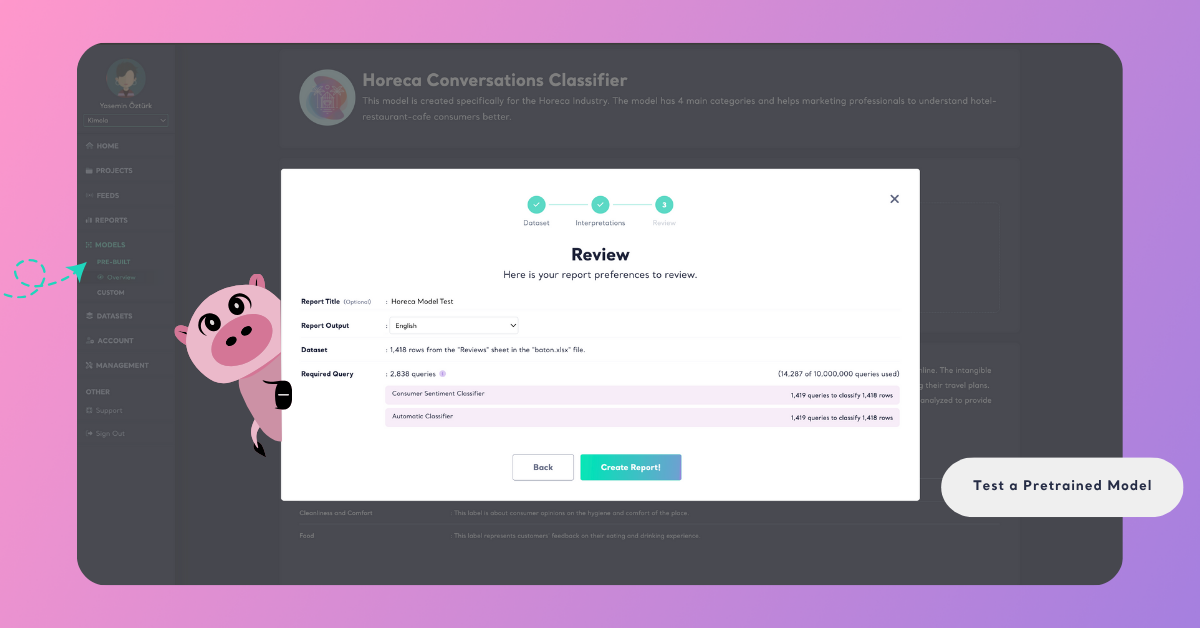
Step 4: Review and Complete the Test
Give your report a name and select the output language of your report. Here, you’ll also see how many rows your dataset contains and how many queries will be required to run the test.
Each row of data (for example, each customer comment) typically consumes one query per model used in the test. If you are running multiple models — such as a Pretrained Classifier and the Automatic Classifier — the total query count will be multiplied accordingly.
Click the info icon next to Required Query to view a detailed breakdown of how many queries your test will use per model.
Testing with a document is especially useful when validating the model’s performance on real-world data before using it in reports or feeds.