How to Calculate Queries?
3 mins read - Updated on May 05, 2025Understanding the concept of queries is essential when performing data analysis on Kimola. This article explains in detail what a query is, when queries are used, how they are calculated, and what to do when you run out of queries.
What Is a Query?
In text analysis software like Kimola, a query is defined as the basic unit of analysis applied to your text data. When you upload a dataset (e.g., an Excel or CSV file), each row containing text is considered one query.
However, there are a few important details that can affect how many queries you actually use:
📏 Character Limit
Each query can contain up to 500 characters.
If a single row exceeds this limit, the system automatically splits it into multiple queries.
For example:
- A row with 800 characters = 2 queries
- A row with 1,200 characters = 3 queries
🧠 Classifiers and Analysis Features
The number of queries used also depends on the analysis features you select during upload:
- Sentiment Classifier → adds 1 query per row
- Automatic Classifier → adds 1 additional query per row
So if you select both sentiment and automatic classification, each row of text (under 500 characters) will count as 2 queries.
📌 Row Count Also Matters
In addition to text length, the number of rows (comments) in your dataset directly affects how many queries are spent.
Let’s say you upload 200 rows of comments:
- Sentiment Classifier → 200 queries
- Sentiment + Auto Classifier → 400 queries (2 queries × 200 rows)
When Do I Spend Queries?
Queries are consumed in two main scenarios on Kimola:
1. Uploading a Custom Dataset
When you upload your own dataset (for example, an Excel or CSV file), each row of text is counted as one query, as long as it does not exceed 500 characters.
- If a row exceeds 500 characters, it is split into multiple queries.
- Selected classifiers will spend 1 query for each review.
Example:

📎 How to Prepare a Custom Dataset
2. Scraping Using Kimola’s Search Bar
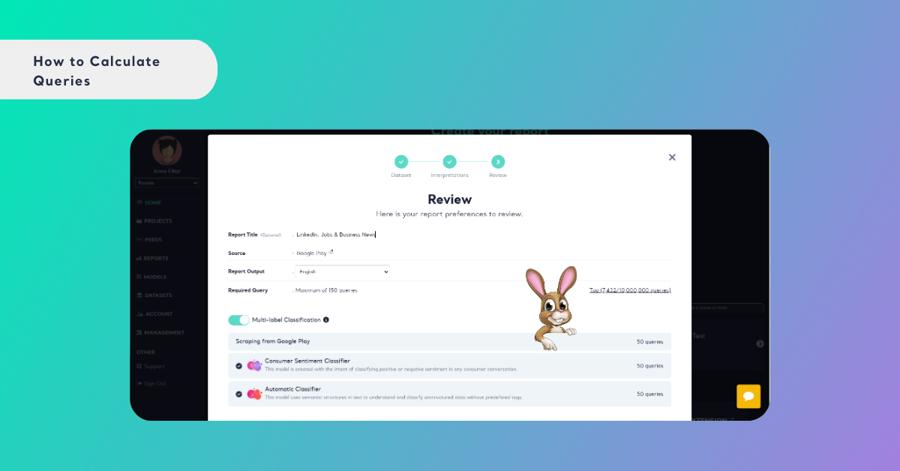
If you’re using Kimola’s built-in search bar to collect data from online platforms (e.g., App Store, Play Store, Google Business ), each piece of scraped content (comment, post, review, etc.) counts as 1 query.
The same rule applies for analysis features: enabling sentiment or automatic classifiers adds additional queries.
Example:

How Can I Track My Query Usage?
Tracking your query usage on Kimola is simple and transparent. Once you upload a dataset or scrape content using Kimola, the system will automatically display:
- The number of items uploaded or collected
- The total character count
- The number of queries consumed, based on the features you selected
This preview allows you to confirm your selections and understand how your query balance will be affected before proceeding.
👉 Now, let’s upload a sample dataset and see how many queries it will use in total.
If your dataset contains more content than your available query balance, only the number of queries you have will be used for analysis. Any excess content will not be analyzed, and no additional charges will be applied. The system does not automatically overcharge or process data beyond your query limit.
If you need to analyze more data than your current query balance allows, you can purchase extra queries at any time. 📎 Learn how to buy extra queries